In the realm of data analysis, where patterns paint stories and numbers speak volumes, Pearson correlation emerges as a powerful tool for quantifying the linear relationship between two variables. Beyond simply stating whether they move together or oppositely, it offers a precise measure of the strength and direction of their connection, empowering researchers and analysts to gain deeper insights from their data.
Beyond Scatterplots: Quantifying the Linear Trend
Imagine studying the relationship between study hours and exam scores. A scatterplot might reveal a general upward trend, but Pearson correlation goes further. It measures the degree to which two variables tend to move in the same or opposite directions. A positive correlation indicates they align (more hours, higher scores), while a negative correlation suggests they move in opposite directions (more hours, lower scores). But wait, there’s more! Unlike a simple slope, Pearson correlation tells you how strong this linear relationship is, ranging from -1 (perfectly negative) to +1 (perfectly positive), with 0 signifying no linear association.
Demystifying the Math: Unveiling the Formula’s Logic
While the mathematical notation of Pearson correlation might seem daunting, the core idea is straightforward:
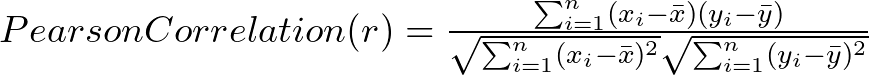
This formula essentially compares the standardized deviations of each data point from its mean, revealing the overall linear trend strength. Don’t worry, most software calculates it automatically, allowing you to focus on interpretation.
Interpreting the Result: Deciphering the Relationship’s Meaning
So, you have a correlation coefficient (r). Now what?
- Strength: Consider the absolute value of r. Values closer to 1 indicate a stronger linear relationship, either positive or negative. Values closer to 0 suggest a weaker or no linear relationship.
- Direction: Remember that positive r means “move together,” while negative r means “move opposite.” Think logically about the variables to ensure the direction aligns with your expectations.
- Caution: Correlation doesn’t imply causation! Just because variables move together doesn’t mean one causes the other. Consider other factors and explore further before drawing causal conclusions.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Diverse Applications
Pearson correlation transcends mere exam scores:
- Finance: Analyzing the relationship between stock prices and economic indicators.
- Social Sciences: Studying the association between income level and educational attainment.
- Biology: Investigating the link between gene expression and disease development.
- Marketing: Assessing the association between advertising campaigns and sales figures.
These diverse applications showcase the versatility of Pearson correlation in understanding connections across various fields.
Important Considerations: Ensuring Accurate Insights
Remember, Pearson correlation has its limitations:
- Linearity: It assumes a straight-line relationship between variables. If the relationship is curved or complex, other measures might be needed.
- Normality: It works best with normally distributed data. Violations can lead to misleading results.
- Outliers: Extreme data points can distort the correlation. Consider outlier analysis if necessary.
By understanding these limitations and applying Pearson correlation responsibly, you can avoid pitfalls and extract valuable insights from your data’s relationships.
Exploring the Broader Statistical Landscape
The world of data analysis offers a plethora of correlation measures:
- Spearman’s rank correlation: Useful for non-normally distributed data or when the relationship is not linear.
- Kendall’s tau: Handles ordinal data (ranked categories) and is robust to outliers.
- Partial correlation: Controls for the influence of other variables when analyzing two specific variables.
Understanding these options expands your toolkit for analyzing diverse relationships within your data.
Empowering Data-Driven Decisions: Unveiling the Power of Relationships
Pearson correlation serves as a valuable tool in your data exploration journey. By grasping its core concepts, applications, and limitations, you can interpret the relationships your data reveals, uncover hidden connections, and make informed decisions in diverse fields. So, embrace the power of data analysis, delve into the world of Pearson correlation, and unlock the secrets hidden within your numbers!
Leave a Reply